What is PA (Polyamide, Nylon)
PA, also known as Polyamide or Nylon, is not only used as a fiber but also has excellent heat resistance, mechanical properties, electrical properties, and chemical resistance. It is also used as an engineering plastic to replace metals, with 35-40% of the total demand being used for automotive and vehicle applications.
Difference between Nylon and Polyamide
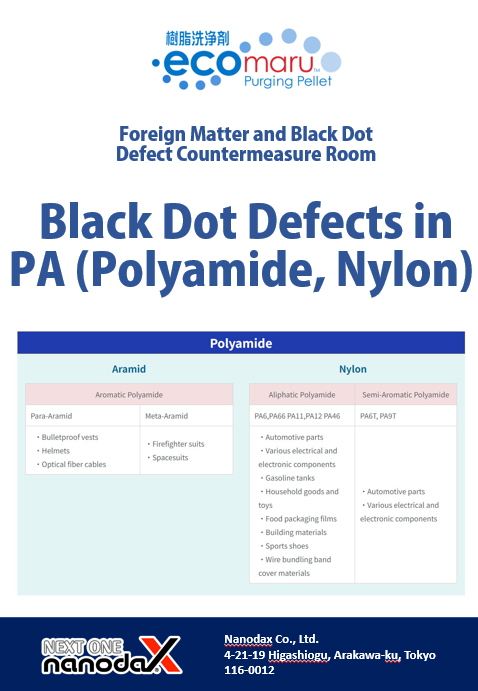
Generally, Nylon and Polyamide refer to the same material. However, if we distinguish them more precisely, there are many types of Polyamides. Those containing an aliphatic backbone are called “Nylon,” while Polyamides consisting only of an aromatic backbone are called “Aramid.”
Polyamide
Aramid
| Aromatic Polyamide | |
|---|---|
| Para-Aramid | Meta-Aramid |
| ・Bulletproof vests ・Helmets ・Optical fiber cables | ・Firefighter suits ・Spacesuits |
Nylon
| Aliphatic Polyamide | Semi-Aromatic Polyamide |
|---|---|
| PA6,PA66 PA11,PA12 PA46 | PA6T, PA9T |
| ・Automotive parts ・Various electrical and electronic components ・Gasoline tanks ・Household goods and toys ・Food packaging films ・Building materials ・Sports shoes ・Wire bundling band cover materials | ・Automotive parts ・Various electrical and electronic components |
- PA6: A synthetic fiber developed by Toray Industries, it is widely used in many garments due to its cotton-like texture.
- PA66: A synthetic fiber first developed by DuPont, it is said to have a texture similar to silk. Among engineering plastics, it boasts excellent mechanical strength, superior to PA6 in both strength and heat resistance.
- PA12: Among polyamides, it has the lowest density and a melting point of 176°C. Compared to PA6 and PA66, it has a lower melting point and water absorption. It is a material with excellent dimensional stability, and its superior properties at low temperatures distinguish it significantly from other types of nylon.
※ The last number in Nylon designations comes from the number of carbon atoms in the synthetic raw materials.
Black dot defect issue in polyamides
One of the troublesome issues with polyamide molding defects is gas generation. While gas generation is not limited to polyamides, it is often caused by insufficient drying due to the high moisture absorption of the resin. Proper drying can mitigate gas generation to some extent. Although black molding usually does not pose significant issues, managing natural (original color) or white molded products becomes more challenging.
In addition to drying the raw material, basic gas countermeasures include degassing and venting in the mold. However, these measures alone may not always solve the problem. In such cases, using purging compounds or performing decompositional cleaning can help remove burning and carbon residues.
Even after cleaning, unresolved black dot defects and issues with replacement after cleaning
【Case 1】
- We are concerned about the frequent occurrence of black dots and foreign matter defects. We perform disassembly and cleaning when the defect rate exceeds 3%.
- We tried various purging compounds but did not achieve significant results, which has been very troubling.
Customer Evaluation
- After trying ecomaru, foreign matter contamination in molded products was drastically reduced, and the defect rate stabilized at 0.1%. This led to a significant improvement in production efficiency.
- It has less odor compared to the purging compounds we used before, which improved the working environment and received positive feedback from the workers.
| Customer Information | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Name | Products Produced | Molding Machine Ton Capacity | Previous Resin Resin | Color | Subsequent Resin Resin | Color | Issues Before Implementation | ||||
| Company A | Industrial Filters | 40 | PA66 | Black | PA66 | White | Reduction of Foreign Matter Defects | ||||
| Before | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purging Compound Name | Usage Amount | Double Cleaning Presence | Black Dot Defect Rate | ||||||
| Company A | Not Disclosed | Yes | 0.5-3% | ||||||
| After | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purging Compound Name | Usage Amount | Double Cleaning Presence | Black Dot Defect Rate | ||||||
| ecomaru GWS | Not Disclosed | No | 0.1% | ||||||
【Case 2】
- We want to reduce the cost of purging compounds.
Customer Evaluation
- The unit price is lower compared to conventional purging compounds.
- The residue of the previous material, which could not be removed with conventional purging compounds, was eliminated, resulting in a halving of foreign matter defects.
- The time required for a single resin change was reduced by about 3 minutes per change, achieving overall cost reduction through a combination of lower unit costs, reduced cleaning time and usage, and decreased defect rates.
| Customer Information | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Name | Products Produced | Molding Machine Ton Capacity | Previous Resin Resin | Color | Subsequent Resin Resin | Color | Issues Before Implementation | ||||
| Company B | Automotive Parts | 1050 | PA6 | Black | PA66 | Black | Cost Improvement | ||||
| Before | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purging Compound Name | Usage Amount | Double Cleaning Presence | Black Dot Defect Rate | ||||||
| Company B | Not Disclosed | PP | 0.35% | ||||||
| After | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purging Compound Name | Usage Amount | Double Cleaning Presence | Black Dot Defect Rate | ||||||
| ecomaru GWS | 10% reduction compared to Before | PP | 0.03% | ||||||
Polyamide Properties
Advantages
- High Wear Resistance
- High Thermal Stability
- Light
- High Durability
- Excellent Oil and Chemical Resistance
- Filling with glass fibers significantly improves strength and rigidity.
- Self-Extinguishing
Disadvantages
- Absorbs Moisture
- Poor Dimensional Stability
Manufacturer
| Manufacturer | Product Name |
|---|---|
| Asahi Kasei Corporation | Leona |
| Ascend Performance Materials Japan Co., Ltd. | BIDINE |
| Arkema Co., Ltd. | Hyprolon 90 / Rilsamid / Rilsan Clear |
| UBE Industries, Ltd. | UBESTA / UBE Nylon |
| EMPLUS Co., Ltd. | E-P Nylon |
| Kuraray Co., Ltd. | GENESTA |
| Solvay Japan Co., Ltd. | TECHNYL / TECHNYL ALLOY / TECHNYL EXTEN / TECHNYL STAR |
| Solvay Specialty Polymers Japan Co., Ltd. | AMODEL Polyphthalamide |
| Takayasu Co., Ltd. | TANAZINE |
| Daicel-Evonik Ltd. | DIAMID / VESTAMID / VESTAMID / TROGAMID |
| Teichu Co., Ltd. | OKILON / TEICHU Nylon |
| Terrabow Co., Ltd. | Terrabow Nylon |
| DuPont Co., Ltd. | Zytel / Minlon |
| DSM Japan Engineering Plastics Co., Ltd. | STANYL / NOVAMID / AKULON |
| Toyo Jushi Co., Ltd. | TOYO Resin |
| Toyobo Co., Ltd. | GLAMIDE |
| Toray Industries, Inc. | AMILAN |
| BASF Japan Ltd. | ULTRAMID |
| Mitsui Chemicals, Inc. | ARLEN |
| Mitsubishi Engineering-Plastics Corporation | RENY |
| UNITIKA Ltd. | ZECOTT / MARANYL / UNITIKA Nylon 6 / UNITIKA Nylon 66 |
| LANXESS Co., Ltd. | DURETHAN |