ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) resin is a type of plastic made from three types of monomers: acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene.
ABS resin is also known as acrylonitrile butadiene styrene resin. As the name suggests, it is made using three types of monomers: acrylonitrile (A), butadiene (B), and styrene (S). Each of these monomers has the following characteristics:
– Acrylonitrile: [characteristics]
– Butadiene: [characteristics]
– Styrene: [characteristics]
- Acrylonitrile: heat resistance, mechanical strength (rigidity), oil resistance
- Butadiene: impact resistance (rubber characteristics)
- Styrene: gloss, moldability (processability), dimensional stability
ABS resin, which combines these characteristics, offers a good balance of mechanical properties and is used in a variety of applications. Additionally, by changing the ratio and bonding methods of each monomer, ABS resin with various properties can be produced.
The history of ABS resin dates back to 1954 when it was first commercialized by US Rubber Company in the United States. There are two main manufacturing methods: the blend type, which blends a styrene-acrylonitrile copolymer with an acrylonitrile-butadiene copolymer, and the graft type, which involves copolymerizing styrene and acrylonitrile in the presence of polybutadiene.
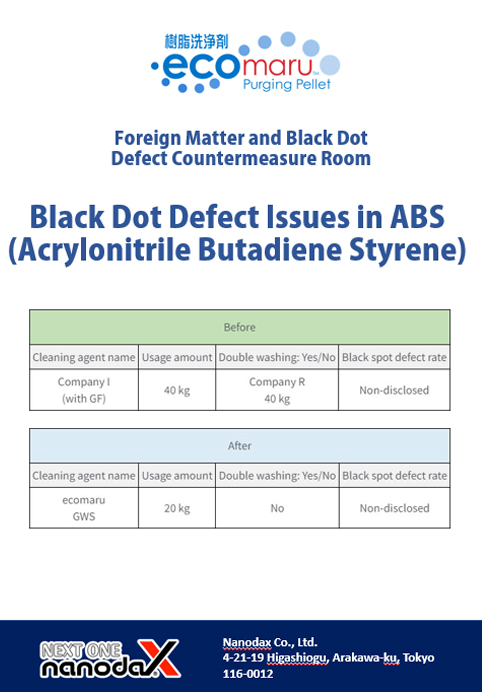
Black dot defect issues in ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
[Case 1]
- Currently, we use a GF-containing purging compound, followed by a double wash with a GF-free purging compound. We want to reduce the amount of purging compound used and setup time.
Customer opinion
- After trying ecomaru, the discharge of the previous material was completed with about half the amount used compared to other GF-containing purging compounds. Additionally, with ecomaru, double washing with another purging compound was unnecessary, reducing the overall purging compound usage by about half.
- With other GF-containing purging compounds, it was necessary to heat up the molding machine before starting the cleaning process, which significantly delayed the start of molding resins with lower molding temperatures. Since ecomaru did not require heating, it greatly reduced the changeover time in this regard.
| Customer information | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customer name | Products | Molding machine Tonnage | Previous resin Resin | Color | Next resin Resin | Color | Challenges before implementation | ||||
| Company A | Home appliance parts | 100 | ABS | Black | PS | Natural | Purging compound usage Setup time reduction | ||||
| Before | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purging compound name | Usage amount | Double washing: Yes/No | Black dot defect rate | ||||||
| Company I (with GF) | 40 kg | Company R 40 kg | Non-disclosed | ||||||
| After | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purging compound name | Usage amount | Double washing: Yes/No | Black dot defect rate | ||||||
| ecomaru GWS | 20 kg | No | Non-disclosed | ||||||
[Case 2]
- Due to production requirements, resins with significantly different colors and molding temperatures had to be molded on the same machine, resulting in frequent contamination and color mixing in the molded products. Although countermeasures were taken each time as the defect rate gradually increased, stabilizing the yield was challenging.
Customer opinion
- After using ECOMAL, various defects were reduced by about half and production efficiency was greatly improved.
- The time required for cleaning was reduced to about 30% compared to other products. Its ease of use also led to a complete switch to ecomaru.
| Customer information | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customer name | Products | Molding machine Tonnage | Previous resin Resin | Color | Next resin Resin | Color | Challenges before implementation | ||||
| Company B | Industrial Equipment parts | 350 | ABS | Black | PP | Black | Improvement of contamination defects | ||||
| Before | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cleansing agent name | Usage amount | Second wash presence | Black dot defect rate | ||||||
| H Company (with GF) | 30Kg | None | 6.00% | ||||||
| After | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cleansing agent name | Usage amount | Second wash presence | Black dot defect rate | ||||||
| ecomaru GWS | 20kg | None | 3.00% | ||||||
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) resin properties
Advantages
- Good balance of mechanical properties
- Strong against external impacts
- Good electrical insulation
- Chemical resistance, strong against weak acids, weak alkalis, and salts
- Excellent cold resistance and relatively high heat resistance, allowing for use over a wide temperature range
- Various properties can be added or modified by adjusting the composition
- Supports various processing methods (machining, bending, welding, bonding, etc.)
- Surface treatments (plating, painting, etc.) can be applied
- Good printing properties
- Adjustable gloss
Disadvantages
- Flammable, burns with a rubber smell and soot
- Weak to organic solvents and dissolves in them
- Absorbs alcohol and hydrocarbons, causing swelling
- Slightly weak to strong acids and strong alkalis, which can cause cracking
- Weak to ultraviolet light, with low weather resistance
Manufacturer
| Manufacturer | Product name |
|---|---|
| Daicel Polymer | Sebian V |
| Chi Mei | Polylac |
| Techno UMG | TECHNO ABS |
| Denka | Denka ABS |
| Toray | Toyolac ABS |
| Japan A&L | Clarastic |
Main applications
Car-related
Car navigation frame, meter case, console box, front grille, handle, etc.
Food-related
Tableware, tray, airtight container, etc.
Home appliance-related
Television, air conditioner, refrigerator, vacuum cleaner, washing machine, pot, PC, laptop, digital camera, printer, game console, etc.
Others
Suitcase, toys, sports equipment, furniture, stationery, musical instruments, etc.