
Causes and countermeasures for black dots in plastic
We provide information on the causes and mechanisms of black dot defects, as well as countermeasures and approaches to address black dot defects.
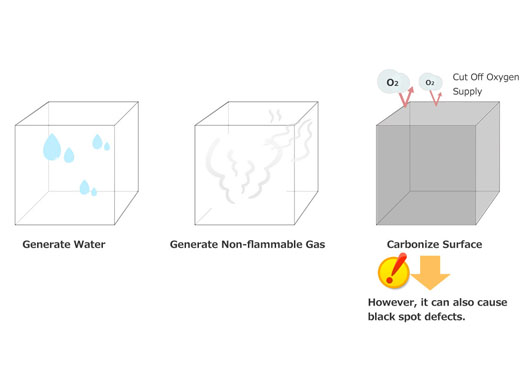
Flame-retardant resin (flame-retardant grade) and black dot defects
Flame-retardant resin (flame-retardant grade) is a type of plastic material that has been enhanced with flame retardants to increase its resistance to burning, thereby improving safety.
POM and molding defects
Polyacetal (POM) resin is a plastic with excellent fatigue resistance. However, it is also one of the more flammable materials and is often reported to suffer from black dot defects in many production sites.
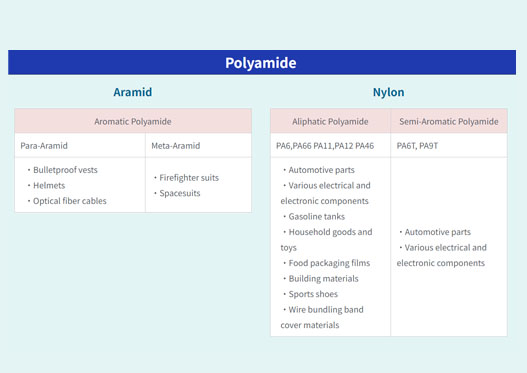
Black dot defect issues in PA (Polyamide, Nylon)
One of the troublesome molding defects in polyamide is caused by gas generation. Due to the high moisture absorption of the resin, insufficient drying is often cited as a common cause of gas formation.
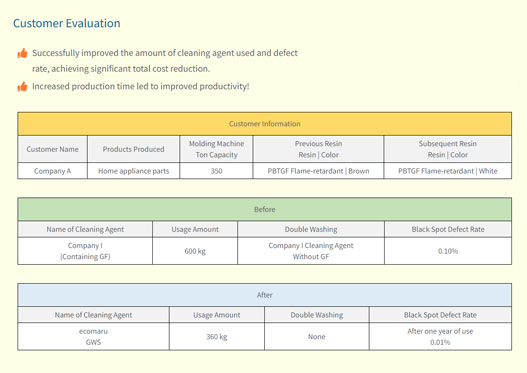
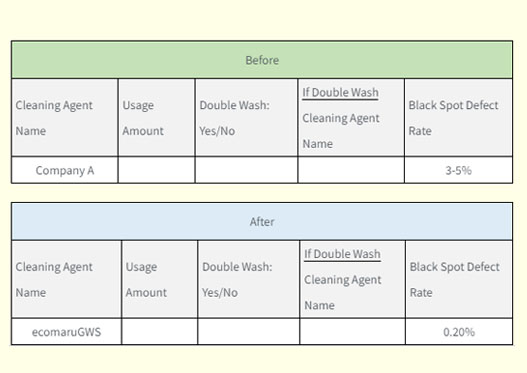
Black dot defect issues in PBT
PBT (Polybutylene Terephthalate) resin is available in many flame-retardant grades from various manufacturers. In molding operations, it is often reported that flame-retardant additives can lead to scorching and carbonization.
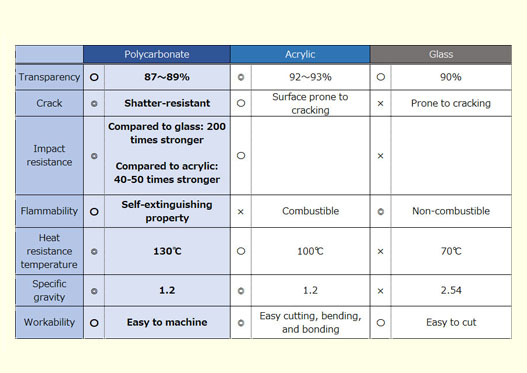
PC (Polycarbonate) and black dot defect issues
Polycarbonate (PC) can create highly precise plastics when blended with ABS resin, but it still faces unresolved black dot defect issues that cannot be eliminated even with thorough cleaning.
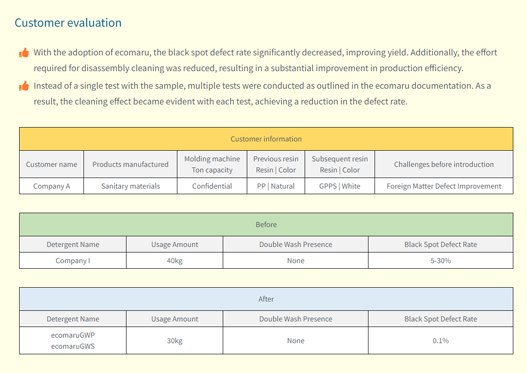
Black dot defect issues in PP (Polypropylene)
Polypropylene is one of the most versatile resins. It is often used for molding, and many problems arise with it.
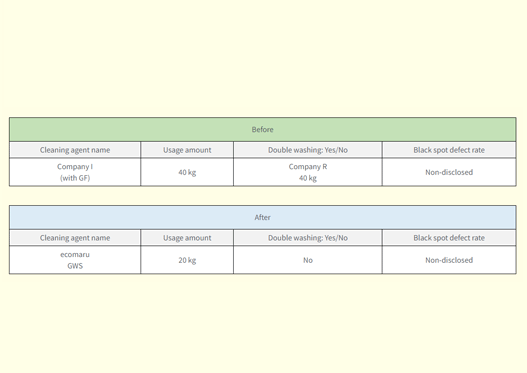
Black dot defect issues in ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
ABS resin is made using three types of monomers: acrylonitrile (A), butadiene (B), and styrene (S).



